2023 興大物件導向程式設計 Test2 歷屆題
簡介與查閱說明
此篇文章為 2023 年 5 月 26 日考的物件導向程式設計的考古題。
更新記錄
- 2024/05/26 發表文章
- 2024/05/26 修正 A6
Q1
Inheritance is also known as the
a. knows-a relationship
b. has-a relationship
c. uses-a relationship
d. is-a relationship
A1
答案:d. is-a relationship
這題在問繼承(Inheritance)代表著物件之間有什麼關係。
舉個繼承的例子:
|
|
在上述例子中,Dog 和 Cat 都繼承父類 Animal,所以它們都可以使用父類的方法:
|
|
除了可以使用父類的方法以外,最能體現物件之間關係的就是在呼叫方法的時候:
|
|
雖然 LetDrink() 方法接收的是 Animal 物件,但我們還是能傳 Animal 的子類:Dog 類進去。
所以我們會說「狗是動物、貓也是動物」,所以這題的答案是 d. is-a relationship。
Q2
Which of the following is not a superclass/subclass relationship?
a. Employee/Hourly Employee.
b. Vehicle/Car.
c. Sailboat/Tugboat.
d. None of the above.
A2
答案:c. Sailboat/Tugboat.
這題在問哪個選項不是父類/子類關係。
a. Employee/Hourly Employee.
這個結構在 Assignment Ch09 中有出現過,Employee 是員工,Hourly Employee 是時薪的員工,在 Ch09 中我們把 Hourly Employee 宣告成 Employee 的子類,所以這個選項是父類/子類關係。
b. Vehicle/Car.
Vehicle 是廣義的車輛,Car 通常是指載送 2~8 名左右乘客/貨物的車輛。這個選項也是父類/子類關係。
c. Sailboat/Tugboat.
Sailboat 是帆船、Tugboat 是拖船。他們並沒有 is-a relationship。所以這個選項不是父類/子類關係。
d. None of the above.
因為有 c 可以選,所以不能選 d 選項。
Q3
Which of the following keywords allows a subclass to access a superclass method even when the subclass has overridden the superclass method?
a. base
b. this
c. public
d. super
A3
答案是:d. super
這題在問我們哪個關鍵字允許我們使用父類的方法(既使子類寫了一個同名的方法 Override 了父類的方法)
super 的用法舉例:
|
|
Q4
Superclass methods with this level of acces cannot be called from subclasses
a. private
b. public
c. protected
d. package
A4
答案:a. private
private 權限的方法只能在同一個類中被呼叫。
關於 Java 的四種訪問權限,請查閱 2022 年 Test1 考古題的第 10 題詳解。傳送門
Q5
Which of the following statement is false?
a. A class can directly inherit from class
Objectb. It’s often much more efficient to create a class by inheriting from a similar class than to create the class by writing every line of code the new class requires.
c. If the class you’re inheriting from declares instance variables as
private, the inherited class can access those instance variables directly.d. A class’s instance variable are normally declared
privateto enforce good software engineering.
A5
答案:c. If the class you're inheriting from declares instance variables as private, the inherited class can access those instance variables directly.
這題在問哪個選項的敘述是錯誤的。
a. 一個 class 可以直接繼承
Object這個 class
這個選項是 true,其實 Java 的所有物件都有隱式地繼承 Object 這個物件,你當然也可以顯式地寫出來:
|
|
至於這個 Java 內建的 Object class 有哪些功能呢?
它總共有 11 個 method,可以自行上網搜尋或參考這個資料
b. 一般來說,繼承一個相似的 class 會比創建一個新物件,然後重寫每一行程式碼還要高效。
這個選項也是 true,畢竟重覆的部分都不用重寫,可以達到程式碼複用。
c. 如果你繼承的 class 有
private權限的 instance variable,繼承完的子類也可以直接訪問這些private的 instance variable 嗎?
這個選項是 false,也就是本題的答案選項。此選項跟 A4 提到的權限問題一樣,不再重覆贅述。
d. 我們通常會將一個 class 的 instance variable 宣告成
private權限,以達到更佳的軟體工程實踐。
這個選項是 true,物件導向 (OOP) 的三大要素:
- 封裝 (Encapsulation)
- 繼承 (Inheritance)
- 多態 (Polymorphism)
其中第一個要素:封裝指的就是盡可能把使用者可以不需要接觸到的部分隱藏起來,避免錯誤的修改與使用。
Q6
Every class in Java, except _______, extends an exsiting class.
a.
Integer
b.Object
c.String
d.Class
A6
答案是:b. Object
剛剛在 A5
的 a 選項提到:所有 Java 中的物件都繼承了 Object 這個類。
所以 Object 自己並沒有繼承別人。
故選 b. Object
Q7
To avoid duplicating code, use _____, rather than ______.
a. inheritance, the “copy-and-paste” approach.
b. the “copy-and-paste” approach, inheritance.
c. a class that explicitly extends
Object, a class that does not extendObject.d. a class that does not extend
Object, a class that explicitly extendsObject.
A7
答案:a. inheritance, the "copy-and-paste" approach.
在繼承 (inheritance) 的時候,父類的 instance variable、實現過的方法 (method) 若沒有特別需要,都不用再重寫一遍,子類都會擁有。所以這題很明顯是選 a.
Q8
Consider the classes below, declared in the same file:
|
|
Which of the statements below is false?
a. Both variables a and b are instance variables.
b. After the constructor for class B executes, the variable a will have the value 7.
c. After the constructor for class B executes, the variable b will have the value 8.
d. A reference of type A can be treated as a reference of type B.
A8
答案:d. A reference of type A can be treated as a reference of type B.
這題在問哪個選項是錯誤的。
先分析一下這個程式碼:
|
|
所以在創建 B 物件時,其實父類 A 的 constructor 也會被呼叫。
知道這些後,接下來就可以來看選項:
a. Both variables a and b are instance variables.
True:a 和 b 都是 instance variable。
b. After the constructor for class B executes, the variable a will have the value 7.
True:在 B 的 constructor 執行時,會隱式地呼叫 super(),也就是父類的 constructor,所以 a 確實會變成 7。
此選項的考點應該是看你會不會誤以為 B 的 constructor 執行時,A 的 constructor 不會被執行。事實上是會。
c. After the constructor for class B executes, the variable b will have the value 8.
True:在 B 的 constructor 可以看到,b 確實會被賦值為 8。
d. A reference of type A can be treated as a reference of type B.
這個選項的意思是:指向 A 的 reference 可以被看作指向 B 的 reference。
更白話講,就是在問這段程式能不能通過編譯:
|
|
答案是當然不能,因為題目把關係講反了。
今天的繼承的關係是 B 繼承 A,所以他們有一個 is-a 的關係,但是是 B is-a A;而非 A is-a B。
換個比較好記的說法:「你會說人跟狗都是動物,但不會說動物都是人,或者動物都是狗吧?」
當今天方法要求接收一個 A 時,我們可以把 B 丟給他,因為 B is-a A,所以 A reference of type B can be treated as a reference of type A.
但選項講的是 A reference of type A can be treated as a reference of type B.,跟繼承關係是相反的,所以此選項為 false。
Q9
Which superclass members are inherited by all subclasses of that superclass?
a.
privateinstance variables and methods.
b.protectedinstance variables and methods.
c.privateconstructors
d.protectedconstructors
A9
答案:b. protected instance variables and methods.
又是 A4
提到的權限問題,只要是 protected 權限的 instance variables 或是 methods 都能被子類繼承。
那為什麼不選 d. protected constructors 呢?看起來也可以啊!…就請先當作要選「最適當的選項」吧。
Q10
The default implementation of method
cloneofObjectperforms a _______.a. empty copy
b. deep copy
c. full copy
d. shallow copy
A10
答案:d. shallow copy
要解這題首先你要了解一個不只是在 Java 中會用到的觀念:「深拷貝 (deep copy) 和淺拷貝 (shallow copy)」
今天如果一個變數是 primitive type:像 int, double, boolean,他們都是直接把資料儲存到電腦的 stack 上面(關於 stack 和 heap 的差別可以參考這類的文章
)
但當你宣告了一個 String 或是為某個 class 創建了物件,這種 reference type 的資料我們動態地在 heap 中找一段空間存放我們的資料,然後把指向這個資料的 reference 壓到 stack 中。
舉個例子,如果有以下變數:
|
|
則在記憶體內部的分配可能是這樣的:
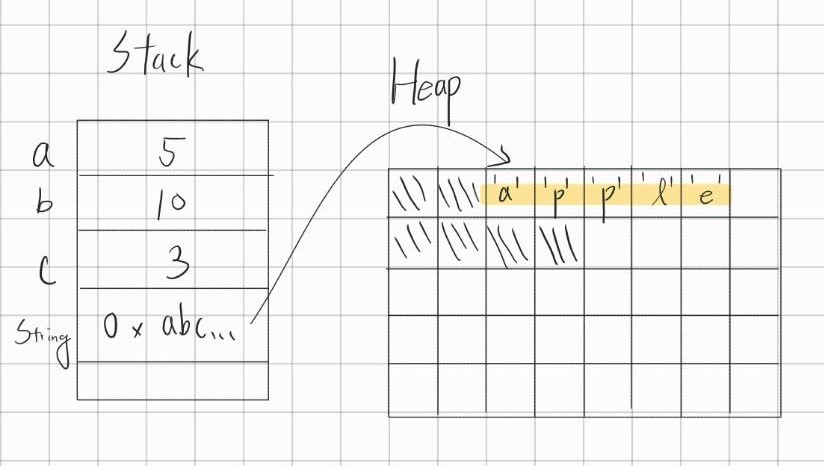
可以看到變數 a, b, c 都直接存在 stack 中,而 String 則是動態在 heap 中找到一段空間後,把字串實際的值儲存到 heap 中、並把字串的 reference 存在 stack 裡面。
那如果今天字串的長度變長了,比如講從 apple 變成 banana 呢?
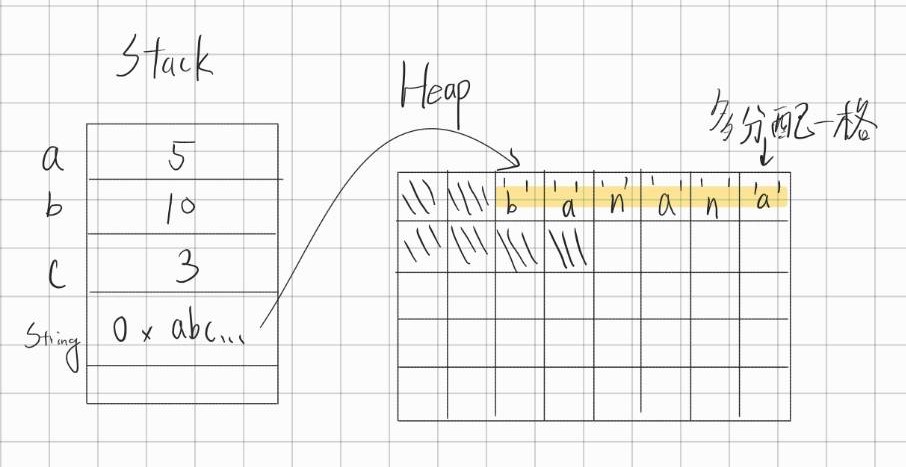
因為後方仍有空間,所以 JVM 很有可能做的事是,把後面那格沒人佔用的空間佔走,這樣就剛好可以放下新的字串了!
那如果我們又再加長字串呢?這次我們讓字串 s = "application":
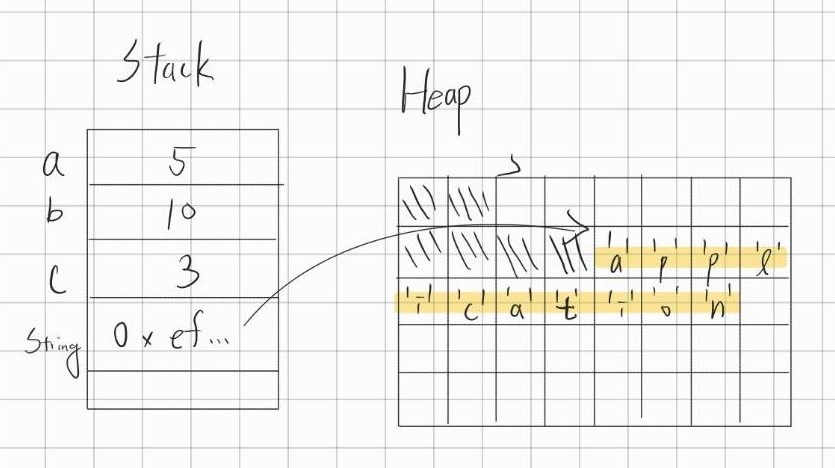
可以看到 JVM 在 heap 中繼續往下找,找了一段更大的空間,在新的地方重新儲存字串的值。在 stack 中儲存的 reference 也跟著發生了改變。
現在我們用 Animal 類來說明 shallow copy 會發生什麼事,你可以猜猜看會印出多少?是 5 還是 0?:
|
|
答案是會印出
|
|
原因就是我們在程式第 8 行的位置:
|
|
並沒有創建一個新的物件,而是把 a 的 reference 複製到了 b 裡面,像這樣:
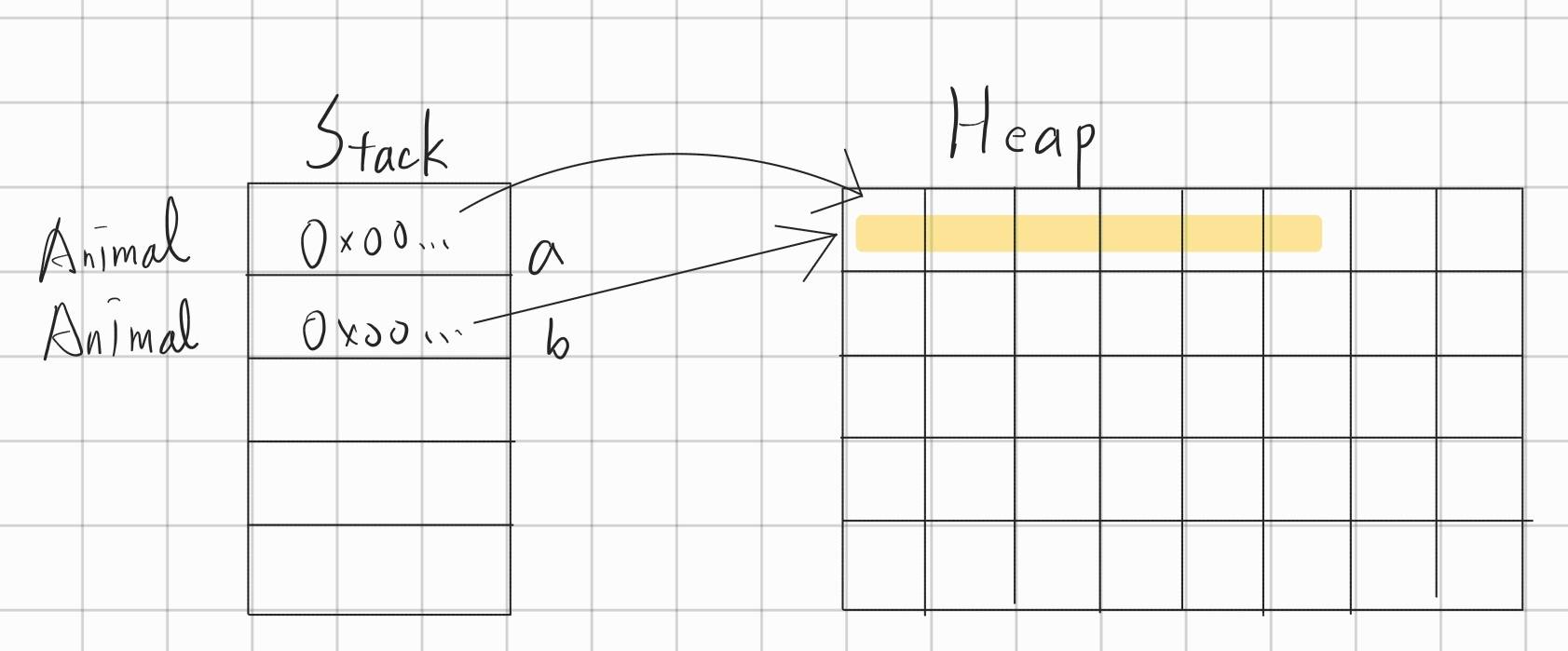
由於 a 和 b 實際上都指向同一個 Animal 物件,所以當我們 a.age = 5,之後取 b.age 時會發現取到的也是 5。
回到題目:
The default implementation of method
cloneofObjectperforms a _______.
預設 Java 會做的就是剛剛講到的淺拷貝而不是深拷貝!
所以答案是 d. shallow copy
Q11
Polymorphism enables you to:
a. program in the general
b. program in the specific
c. absorb attributes and behavior from previous classes
d. hide information from the user
A11
答案:a. program in the general
這題在問多態 (Polymorphism) 這個功能可以做什麼。
直接舉例子大家應該就懂了:
|
|
在這個例子中,我們宣告了 Student 作為父類,並且讓 CollegeStudent 和 ElementaryStudent 繼承 Student。
於是乎身為家長,如果你的家裡同時有兩個小學生和三個大學生,你要叫他們去寫作業就可以一視同仁:
|
|
很明顯,大學生和小學生寫的作業內容一定不一樣,但是身為亞洲家長的我們只需要:「快去寫作業!!!」,不同的學生就會依照自己實現的方法,完成不同種類的作業,這就是多態。
所以答案是 a. program in the general,我們可以統一調用一樣的函數名就好!
Q12
Polymorphism allows for specifics to be dealt with during:
a. execution
b. compliation
c. programming
d. debugging
A12
答案:a. execution
就像剛剛 A11
提到的那樣,在執行時程式會根據實際對象的不同(CollegeStudent/ElementaryStudent)自動進行不同的操作。
Q13
A(n) ____ class cannot be instantiated.
a. final
b. concrete
c. abstract
d. polymorphic
A13
答案:c. abstract
abstract 是指抽象化,當宣告 abstract 的時候,代表目前這個類本身不會被實例化 (Instantiate),用剛剛 A11 的程式來舉例:
|
|
如果我們不希望 Student 類被創建物件出來,但我們又需要他作為 CollegeStudent 和 ElementaryStudent 的父類,就可以把 Student 宣告成 abstract 類,而且 Student 中的 DoHomework 方法也可以宣告成 abstract,不用實現:
|
|
在這種情況下,宣告成 abstract 的 Student 類並能被實例化(Instantiated),也就是不能創建 Student 物件。
所以答案是 c. abstract
Q14
It is a UML convention to denote the name of an abstract class in _______.
a. bold
b. italics
c. a diamond
d. there is no convention of the UML to denote abstract classes - they are listed just as any other class.
A14
答案是:b. italics (斜體)
這題在問 UML 圖在表達 abstract class 的時候通常會怎麼註記。
UML 圖是用來描述你的程式系統、類、功能之間的關係,有一點點像是流程圖那樣,但是是描述結構而非運作流程。
有關 UML 的資料可以參考這裡 。
這題的答案就…記起來吧。
Q15
Which of the following could be used to declare abstract method method1 in abstract class Class1 (method1 returns an int and takes no arguments)?
a.
public int method1();
b.public int abstract method1();
c.public abstract int method1();
d.public int nonfinal method1();
A15
答案:c. public abstract int method1();
根據題目可以看到有幾個要求:
- 是 abstract 的方法:所以會有 abstract 關鍵字出現
- 方法名叫作 method1
- 方法會 return int,而且不接收參數
讓我們來看看每個選項:
a.
public int method1();
這個選項沒有 abstract 字樣,所以可以刪掉。
d.
public int nonfinal method1();
似乎根本沒有 nonfinal 這個關鍵字,所以不考慮這個選項。
b.
public int abstract method1();
c.public abstract int method1();
看來只剩這兩個選項,他們只差在 abstract 和 int 的順序而已。
Java 的關鍵字順序是有規定的:
- 先寫權限,比如
public,protected,private - 再寫其它關鍵字,比如
static,final,abstract - 接著寫 return 的類型,比如
int - 最後才寫 method 的名稱,像
method1
所以這題要選 c. public abstract int method1();
Q16
When a superclass variable refers to a subclass object and a method is called on that object, the proper implementation is determined at execution time. What is the process of determining the correct method to call?
a. early binding
b. non-binding
c. on-time binding
d. late binding
A16
答案:d. late binding
題目翻譯:「如果有一個父類的變數,指向子類的類別。然後我們呼叫這個變數的方法,Java 判斷要執行父類/子類的方法的過程稱為什麼?」
舉個例子,先宣告父類 Animal 和子類 Dog、Cat:
|
|
接著我們按照題目說的,宣告一個父類(Animal)變數,並讓它指向子類的物件(Dog、Cat):
|
|
像這種在編譯的時候沒辦法知道應該呼叫誰,要在執行時才知道結果的程式,我們叫它 late binding(延後綁定)。
所以答案為 d. late binding
Q17
Classes and methods are declared final for all but the following reasons:
a. final methods allow inlining the code
b. final methods and classes prevent further inheritance
c. final methods are static
d. final methods can improve performance
A17
這題在問「把類和方法宣告成 final 的理由,不包含哪個選項?」
a. final methods allow inlining the code
d. final methods can improve performance
這兩個選項可以一起看。
Inlining(內聯展開)的相關資料可以參考維基百科 。
簡單來說,當一個類或者方法被宣告成 final,代表他們在初始化之後就不會再變動,JVM 有可能會幫我們進行內聯,也就是像這樣:
|
|
直接把那個值、或是方法的程式碼替換到我們呼叫它的地方。這樣做也可以增加程式的運行效能。
b. final methods and classes prevent further inheritance
當一個 class 被宣告成 final 時,就不能繼承它。
以下這段程式碼會無法通過編譯:
|
|
c. final methods are static
final指的是宣告的方法/類/變數在被初始化之後,就不能改變static通常用在方法上,被宣告成static的方法是整個class共用的
這兩個是不同的觀念,所以這個選項是 false
|
|
Q18
In Java SE 7 and earlier, an interface may contain:
a. private static data and public abstract methods
b. only public abstract methods
c. public static final data and public abstract methods
d. private static data and public final methods
A18
答案:c. public static final data and public abstract methods
介面 (Interface) 的用法在 Java 的不同版本中略有不同,所以這題才要強調是 Java SE 7 及更早的版本。
首先你要了解為什麼我們需要 Interface。我們舉個例子,首先我們寫一個 Animal 類,並且讓 Person、Dog 和 Cat 都繼承它。其中 Animal 有一個方法是 sleep(),因為基本上是動物都會睡覺。
|
|
接著我們用一個 Animal 型態的陣列把一個人、一隻狗和一隻貓存起來,並叫他們都睡覺:
|
|
目前為止都很正常對吧?到了夜深人靜的時候,可能人、狗、貓都需要睡覺了,所以可以用這種方式來呼叫所有的 Animal 物件睡覺。
但並不總是所有物件都有 is-a 關係,舉例來說,你有一台電腦,電腦也有一個方法叫作 sleep(),為了響應節能減碳,你希望晚上的時候電腦可以跟你一起 “sleep”,不要用太多電:
|
|
現在問題來了,Computer 並沒有辦法放到我們的 Animal[] 陣列裡面,因為很明顯它沒有繼承 Animal 類。
但如果要讓 Computer 繼承 Animal 的話又很奇怪,因為電腦不是一種動物…至少在人工智慧大崛起之前。
現在就是 interface 派上用場的時候了!
|
|
接著回去修改我們的類,因為我們的所有類都有實現 sleep() 方法,所以他們可以直接寫上 implements ISleep:
|
|
接著我們就可以在主程式中,改用 ISleep 類型的陣列來儲存所有動物、電腦,統一讓他們睡覺了!
|
|
其實 Interface 的功用還有很多,在此不細講。
現在你知道 Interface 有什麼用之後,我們回到正題,還記得剛剛寫介面程式的時候出現過這段嗎?
|
|
有沒有覺得少了點什麼?沒錯,我的 sleep 方法並沒有加上 public 的關鍵字。
事實上在 Java SE 7 以及之前的版本,Interface 裡面只會有兩種東西:
public static final的資料- 當你在介面裡面指定任何
implements介面的人都要有某個資料 (eg.age),則這個資料一定是public static final
- 當你在介面裡面指定任何
public abstract的方法- 當你在介面裡面指定任何
implements介面的人都要有某個方法 (eg.sleep()),則這個方法一定是public abstract
- 當你在介面裡面指定任何
所以事實上:
|
|
所以答案是 c. public static final data and public abstract methods
那如果是別的版本呢?新增了什麼
- JavaSE 8
- 允許你在 Interface 裡面定義
static的方法 - 允許你寫預設方法 (default methods),也就是在介面裡面可以寫出方法具體的程式碼,當
implements的人不特別@Overeride時,就會直接擁有介面中實作的方法
- 允許你在 Interface 裡面定義
- JavaSE 9
- 允許你在介面中定義
private的方法,主要是用在介面內部如果有邏輯要共享時(因為 JavaSE8 開始可以在介面裡面實作邏輯)
- 允許你在介面中定義
Q19
Interfaces can have _____ methods
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. any number of
A19
答案:d. any number of
Interface 並沒有特別限制只能有幾個方法,所以選 d. any number of
Q20
A class that implements an interface but does not declare all of the interface’s methods must be declared _______
a. public
b. interface
c. abstract
d. final
A20
答案:c. abstract
這題在問「如果有個 class 聲明要 implements 某個介面,但是它卻沒有把介面內要求的方法實作/宣告出來,則這個 class 應該宣告成 public/interface/abstract/final?」
先用 class 之間的繼承來舉例:
|
|
在這個例子中,Human 繼承 SmartAnimal,SmartAnimal 繼承 Animal。
其中 SmartAnimal 雖然繼承了 Animal,但他依然沒有實作 Animal 中的 eat 方法,所以還是要宣告成 abstract。
聰明的你應該想到了,換成介面也是一樣:
|
|
所以此題答案選 c. abstract
 Junqi's Blog
Junqi's Blog